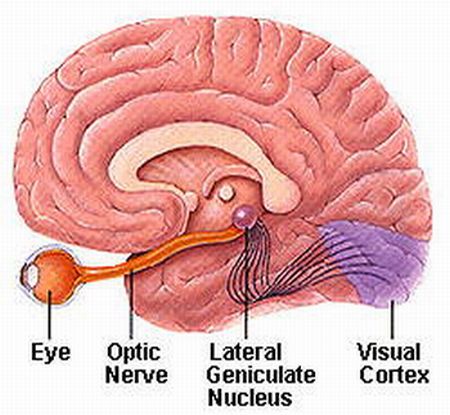
Optic neuritis, or the inflammation of the optic nerve that connects the eye to the brain, is the third most common type of multiple sclerosis relapse, making up approximately 17% of all attacks. 20% of all MSers experience this as their first acute attack. The optic nerve sends messages from the eye to the brain, describing visual clarity, color perception, and brightness. An attack of optic neuritis usually affects one eye. During an acute MS optic nerve attack (when the immune system attacks the myelin covering surrounding the optic nerve), the following symptoms may occur:
Blurred, murky vision: this can be intermittent or it can be a steady disruption of proper sight
Acute loss of vision: complete loss of vision in the affected eye may occur, and this too may fluctuate or remain steady during an attack
Eye pain: pain from the inflamed optic nerve can make moving the eye or even keeping the eye still very painful
Loss of or change in color vision: optic nerve inflammation can also cause a loss of or fluctuation in color clarity, making the visual field less vivid or “washed out”

